Guinea mining potential
BAUXITE : 40 billion tons in Boké, Fria, Gaoual, Télimélé, Pita-Labé, Mali, Kindia, Dabola, Tougué, Lelouma, Mamou, Dalaba, Koubia,
IRON ORE : More than 25 billion tons (Beyla, Kérouané, N’Zérékoré, Macenta, Lola, Gaoual, Faranah and Forécariah)
GOLD : Several thousand tons mainly in the Birimian Guinean basin (Siguiri, Mandiana, Kankan, Dinguiraye, Dabola, Kouroussa)
DIAMOND : More than 10 million carats (Kérouané, Macenta, Kissidougou, Beyla, Forécariah, Télimélé and Kindia)
LIMESTONE : Hundreds of millions of tons in the prefectures of Kindia, Mali and Siguiri.
URANIUM : Potential existence yet poorly evaluated, in the research stage in the prefectures of Kissidougou, Kérouané, Mandiana, Mali and Beyla.
BASE METALS : Does not display economic value at present but very strong clues of existence, at the geological and mining research stage: Faranah, Boké, Télimelé, Dubreka, Kindia, Kérouané, Kissidougou, N’Zérékoré, Yomou and Beyla
BUILDING MATERIALS : Building materials can be found everywhere with inexhaustible reserves of sand, laterite, gravel, pisolite, clay, granite, ornamental granites
Source: Strategy and Development Department – Ministry of Mines and Geology (2015)
Sector Overview: Mining
Main growth sector like the agriculture and energy sectors, the Guinean mining sector has some of the largest reserves of mineral

resources in the world: bauxite (+ 40 billion tons of bauxite containing AI203 40%), iron ore (+ 10 billion tons of high-grade ore), gold (many thousands of tons), Diamond (mainly of jewelery quality) as well as possible clue of uranium, graphite, copper and petroleum.
The Guinea mining sector accounts for 12 to 15% of the GDP:
Gold: more than 700,000 ounce per year (among the top ten (10) of African producers)
Diamond: 700,000 carats on average per year (2010-2015, small-scale artisanal exploitation)
(Macroeconomic forecasting framework data)
Thus, Guinea is set to make full use of its mining potential.
Overview
The country’s mining potential is still being underexploited
Since 2013, the Government has adopted a new policy with the objective of providing maximum profit incentives to investors, extending the volume of tax revenues and promoting local added value
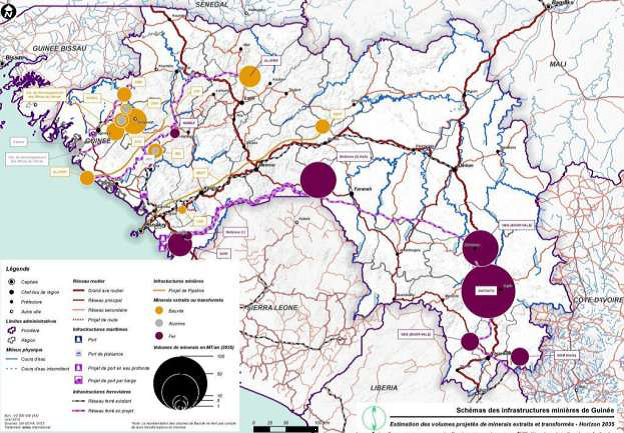
through five (5) axes: (1) step up geological research; (2) encourage local processing; (3) restructure and strengthen semi-public mining companies undergoing difficulties, (4) promote private investments, (5) continue with legal, fiscal and institutional reforms in the sector.
Lots of efforts have been made to strengthen the regulatory and governance framework as part of the strategy to make mining a key sector for socioeconomic development of Guinea. This strategy will undoubtedly facilitate major investment opportunities in the Guinean mining sector.
Many mining exploitations are ongoing (CBG, CBK, ANGLO GOLD, SMD, SMB, etc.), many projects like the processing and exporting of iron ore (RIO TINTO) are in the development stage. Great opportunities in infrastructure development will evidently open up (railways, roads, regional airports, ports, housing, etc.)

Competitive advantages
The diversity, quality and immense concentration of mineral resources in Guinea’s subsoil is a
remarkable feature, hence the adjective “geological scandal” when referring to the country. The country has major natural assets: a coastline of more than 300 km along the Atlantic Ocean and a hydro energy potential of 600 MW.
Opportunities in brief
Bauxite and Aluminum
Second largest exporter in the world, Guinea has 2/3 of the world’s bauxite reserves.
The Northwestern region attracts leading and medium-sized bauxite / alumina companies: Compagnie des Bauxite Guinée (CBG), Compagnie des Bauxite de Kindia (CBK), Guinea Alumina Corporation, Alcoa/Rio Tinto, China Power Investment, and more. These projects are in various exploitation or negotiation phases.
Iron Ore
In Southeastern Guinea, the Simandou chain contains one of the largest untapped high-grade iron ore resources. Simandou is also currently running the biggest mine, rail and port infrastructure project in the world. The project is being developed in partnership with the Guinean Government, Rio Tinto, Chalco and the IFC (World Bank): 650 km of railway for passengers and freight services; major reconstruction of the road networks; a deep sea port designed to accommodate boats of 250 000 to 300 000 tons; telecommunications infrastructure along the railway line; direct investment to support businesses and build the capacities of local workers.

Gold and Diamond
The Northeastern part of Guinea contains a significant gold deposit. The most prospective zones are: Siguiri, Dinguiraye, Kouroussa and Mandiana with the presence of big players like Societe Miniere de Dinguiraye (SMD – Russian) and AngloGold. The overall potential is estimated at over 10,000 tons of gold.
Guinea also has significant diamond deposits located mainly in Upper Guinea and Forest Guinea along the Baoulé, Milo, and Diani Rivers. Other reserves were discovered on the west coast of the country. Total resources are currently estimated between 25 and 30 million carats, and the potential remains undetermined.
For more information, visit the official website of the Ministry of Mines and Geology: www.mines.gov.gn


